Indentation of row labels is an effective way for establishing structure in a
table stub. tab_stub_indent() allows for fine control over row label
indentation in the stub. We can use an explicit definition of an indentation
level (with a number between 0 and 5), or, employ an indentation
directive using keywords ("increase"/"decrease").
Arguments
- data
The gt table data object
obj:<gt_tbl>// requiredThis is the gt table object that is commonly created through use of the
gt()function.- rows
Rows to target
<row-targeting expression>// requiredThe rows to consider for the indentation change. We can supply a vector of row ID values within
c(), a vector of row indices, or use select helpers here (e.g.starts_with(),ends_with(),contains(),matches(),num_range(), andeverything()). We can also use expressions to filter down to the rows we need (e.g.,[colname_1] > 100 & [colname_2] < 50).- indent
Indentation directive
scalar<character|numeric|integer>// default:"increase"An indentation directive either as a keyword describing the indentation change or as an explicit integer value for directly setting the indentation level. The keyword
"increase"(the default) will increase the indentation level by one;"decrease"will do the same in the reverse direction. The starting indentation level of0means no indentation and this values serves as a lower bound. The upper bound for indentation is at level5.
Compatibility of arguments with the from_column() helper function
from_column() can be used with the indent argument of tab_stub_indent()
to obtain varying parameter values from a specified column within the table.
This means that each row label could be indented a little bit differently.
Please note that for this argument (indent), a from_column() call needs
to reference a column that has data of the numeric or integer type.
Additional columns for parameter values can be generated with cols_add()
(if not already present). Columns that contain parameter data can also be
hidden from final display with cols_hide().
Examples
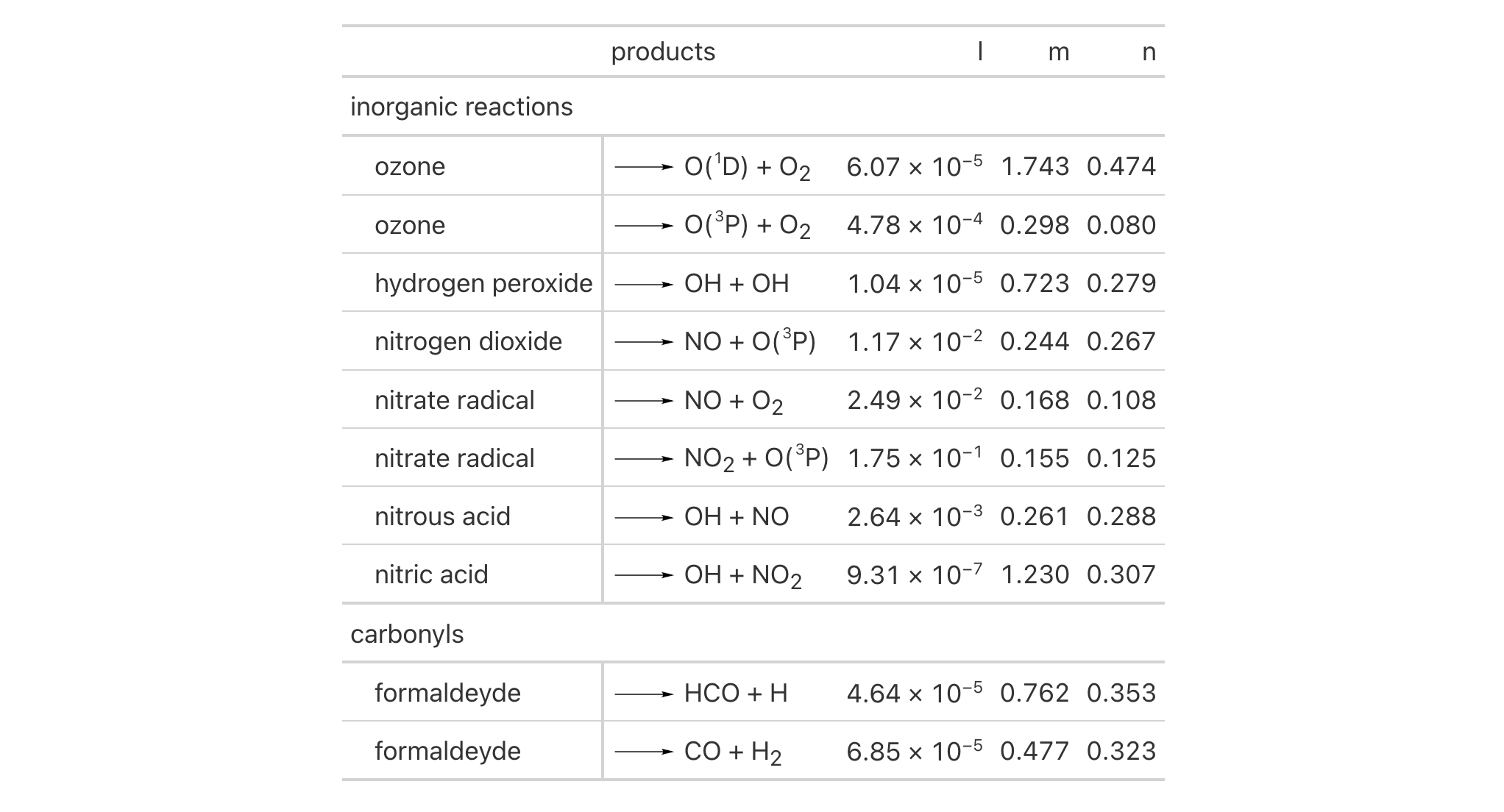
Using a subset of the photolysis dataset within a gt table, we can
provide some indentation to all of the row labels in the stub via
tab_stub_indent(). Here we provide an indent value of 3 for a very
prominent indentation that clearly shows that the row labels are subordinate
to the two row group labels in this table ("inorganic reactions" and
"carbonyls").
photolysis |>
dplyr::select(cmpd_name, products, type, l, m, n) |>
dplyr::slice_head(n = 10) |>
gt(groupname_col = "type", rowname_col = "cmpd_name") |>
fmt_chem(columns = products) |>
fmt_scientific(columns = l) |>
tab_stub_indent(
rows = everything(),
indent = 3
)
Let's use a summarized version of the pizzaplace dataset to create a
another gt table with row groups and row labels. With summary_rows(),
we'll generate summary rows at the top of each row group. Using
tab_stub_indent() we can add indentation to the row labels in the stub.
pizzaplace |>
dplyr::group_by(type, size) |>
dplyr::summarize(
sold = dplyr::n(),
income = sum(price),
.groups = "drop"
) |>
gt(rowname_col = "size", groupname_col = "type") |>
tab_header(title = "Pizzas Sold in 2015") |>
fmt_integer(columns = sold) |>
fmt_currency(columns = income) |>
summary_rows(
fns = list(label = "All Sizes", fn = "sum"),
side = "top",
fmt = list(
~ fmt_integer(., columns = sold),
~ fmt_currency(., columns = income)
)
) |>
tab_options(
summary_row.background.color = "gray95",
row_group.background.color = "#FFEFDB",
row_group.as_column = TRUE
) |>
tab_stub_indent(
rows = everything(),
indent = 2
)
Indentation of entries in the stub can be controlled by values within a
column. Here's an example of that using the constants dataset, where
variations of a row label are mutated to eliminate the common leading text
(replacing it with "..."). At the same time, the indentation for those rows
is set to 4 in the indent column (value is 0 otherwise). The
tab_stub_indent() statement uses from_column(), which passes values from
the indent column to the namesake argument. We hide the indent column
from view by use of cols_hide().
constants |>
dplyr::select(name, value, uncert, units) |>
dplyr::filter(
grepl("^atomic mass constant", name) |
grepl("^Rydberg constant", name) |
grepl("^Bohr magneton", name)
) |>
dplyr::mutate(
indent = ifelse(grepl("constant |magneton ", name), 4, 0),
name = gsub(".*constant |.*magneton ", "...", name)
) |>
gt(rowname_col = "name") |>
tab_stubhead(label = "Physical Constant") |>
tab_stub_indent(
rows = everything(),
indent = from_column(column = "indent")
) |>
fmt_scientific(columns = c(value, uncert)) |>
fmt_units(columns = units) |>
cols_hide(columns = indent) |>
cols_label(
value = "Value",
uncert = "Uncertainty",
units = "Units"
) |>
cols_width(
stub() ~ px(250),
c(value, uncert) ~ px(150),
units ~ px(80)
) |>
tab_style(
style = cell_text(indent = px(10)),
locations = list(
cells_column_labels(columns = units),
cells_body(columns = units)
)
)
See also
Other part creation/modification functions:
tab_caption(),
tab_footnote(),
tab_header(),
tab_info(),
tab_options(),
tab_row_group(),
tab_source_note(),
tab_spanner(),
tab_spanner_delim(),
tab_stubhead(),
tab_style(),
tab_style_body()